Table of Contents
2. What is protactinium used for?
3. Who discovered protactinium?
4. Where is protactinium found?
What is protactinium?
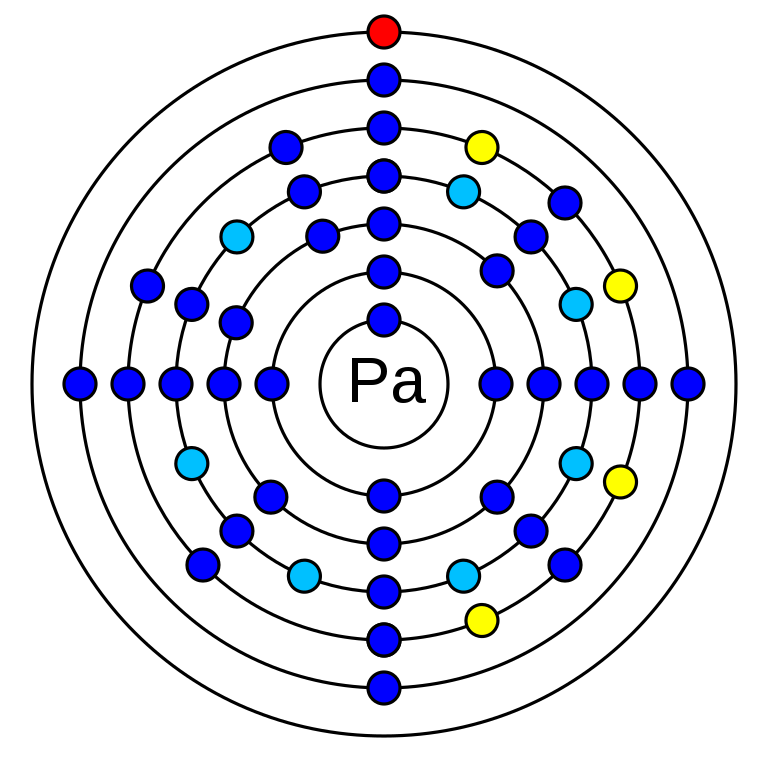
Protactinium is a chemical element that has the atomic number 91. Its atomic mass is 231.035 g/mol and it is represented by the symbol Pa. Protactinium is an f-block element and a member of the actinide series. It is in period 7 of the periodic table after thorium. Its electronegativity is 1.5 (Pauling scale) and its oxidation states are +2, +3, +4, +5. The electronic configuration of Protactinium is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p6 5f2 6d1 7s2. It has 91 electrons and 140 neutrons. Protactinium has no stable isotopes. Standard atomic weight is given on the basis of three naturally occurring isotopes which are radioisotopes. The long-lived among them is the Pa-231 isotope which half-life is 32,760 years.
At STP it is in solid-state and has a density of 15.37 g/cm3. It has a bright, silvery metallic luster appearance. At any temperature, no magnetic transitions are known for protactinium. It is paramagnetic in nature. Its melting point is 1841 K ?(1568 °C, ?2854 °F) and its boiling point is 4300 K ?(4027 °C, ?7280 °F.
The existence of Protactinium was predicted by the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. It was placed between thorium and Uranium. One of the isotope Pa-234 was discovered and isolated by Kasimir Fajans and Oswald Helmuth Göhring in 1913.
It is one of the rarest naturally occurring elements. It can be extracted from ore like uraninite and a significant amount from bentonite. Radioactive decay of uranium is the major source of Protactinium. In nuclear reactors, it is obtained and produced from thorium ( Pa-231 and Pa-233).
Protactinium is in between thorium and Uranium, both has a wide range of application. Its scarcity makes it difficult to use even for experimental use. In geology and paleoceanography it is used as a tracer for radiometric dating of sediments.
What is protactinium used for?
In geology and paleoceanography, it is used as a tracer for the radiometric dating of sediments. Its scarcity and radioactivity make it difficult to use even for experimental use.
Who discovered protactinium?
Protactinium was predicted and placed between thorium and uranium by the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. Then in 1913 Kasimir Fajans and Oswald Helmuth Göhring discovered isotope Pa-234 of Protactinium while studying decay chains of uranium-238. They named it brevium (Latin Brevis meaning short) because Pa-342 has a short half-life, 6.7 hours. Later on, two groups of scientists from Germany (Otto Hahn and Lise Meitner) and Britain (Frederick Soddy and John Cranston) discovered the relatively long-lived half-life ( 33,000 years) isotope Pa-231. The name brevium was changed to protoactinium.
Where is protactinium found?
It can be extracted from ore like uraninite and a significant amount from bentonite. Radioactive decay of uranium is the major source of Protactinium. In nuclear reactors, it is obtained and produced from thorium ( Pa-231 and Pa-233). It is one of the rarest naturally occurring elements.