Table of Contents
1. Atoms with varying number of Neutrons:
2. Isotone:
4. How do isotopes of an element differ?
5. What is a radioactive isotope?
Atoms with varying number of Neutrons:
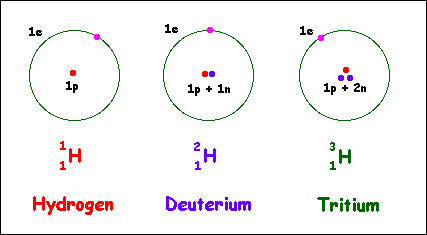
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that has the same atomic number but different atomic mass. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that has the same atomic number because they had the same number of protons. While they had different atomic masses because they had a different number of neutrons in the nucleus. Isotopes of the same elements have almost similar chemical properties but different physical properties.
Carbon has three isotopes Carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14. All these three isotopes have the same atomic number 6 which means they all had the same number of protons. But they had different atomic masses which means they had different numbers of neutrons.
Carbon-12 has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, Carbon-13 has 6 protons and 7 neutrons while Carbon-14 has 6 protons and 8 neutrons.
This example can also be applied to three isotopes of Hydrogen which are Protium, Deuterium, and Tritium (Practice it).
Some related words;
Isobar: (Greek: isos, meaning "equal" and baros, meaning "weight".)
Isobars are atoms of different elements having the same atomic mass but different atomic numbers. It is also called nuclide. Some of the examples of isobars are Sulfur-40, Chlorine-40, Argon-40, Potassium-40, and Calcium-40.
Isotone:
Two or more atoms have the same number of neutrons but different numbers of protons.
For example, carbon-13 and Boron-12 both have 7 neutrons. But a different numbers of protons, Boron-12 has 5 protons and carbon-13 has 6 protons. These are isotones.
FAQs
What is an isotope?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
How do isotopes of an element differ?
Because they have different numbers of neutrons. This means they had different atomic masses.
What is a radioactive isotope?
A radioisotope is an isotope that has excess nuclear energy. The excess energy makes it unstable the energy is then released in different forms of radiation.