Table of Contents
3. What is the basis of a metallic bond?
4. What holds the positively charged metal ions together within a metallic bond?
5. Which factor distinguishes a metallic bond from an ionic bond?
Metallic Bonding:
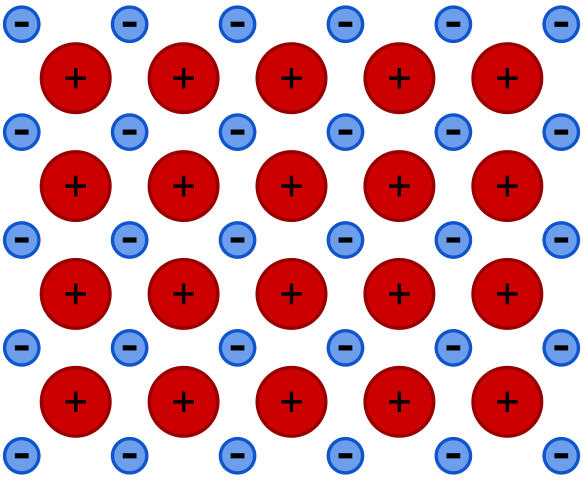
It is a type of chemical bonding which occurs between metals. Metals are electropositive; they tend to lose one of their valence electrons to attain a stable electronic configuration. In a metallic crystal, atoms are packed closely together. The outermost electrons become delocalized due to low electrons affinity. This delocalization produced positive ions surrounded by a sea of valence electrons that binds positively charged metal ions. There is an electrostatic force of attraction between electrons and positively charged metal ions. These valence electrons act as glue binding metal ions together through metallic bonding.
Metallic bonding is the reason for some of the physical properties of metals such as thermal and electrical resistivity and conductivity, luster, strength, and ductility. Metals are strong but not rigid and they are malleable which means they can be hammered into different shapes. They are ductile meaning can be pulled out into wires.
FAQs
What is a metallic bond?
It is a type of chemical bond in which metals are bound to each other through an electrostatic force of attraction between positively charged metal ions and delocalized valence electrons. Metallic bonds occur between metals.
What is the basis of a metallic bond?
Metals are electropositive having loose valence electrons. They have very low ionization energy and electron affinity. Metals try to attain stable electronic configuration by losing one or more of their valence electrons. the outermost electrons become delocalized. Making a sea of mobile valence electrons which binds the ions together. These electrons act as glue between positively charged metal atoms. There is an electrostatic force of attraction between delocalized electrons and positively charged metal atoms.
What holds the positively charged metal ions together within a metallic bond?
There is a force of attraction (electrostatic force of attraction) between delocalized electrons and positively charged metal ions.
Which factor distinguishes a metallic bond from an ionic bond?
A metallic bond is based on the electrostatic force of attraction between delocalized electrons and positively charged metal ions. While an ionic bond is between two atoms one loses an electron (electropositive) to another atom (electronegative) and binds together through an electrostatic force of attraction. Both atoms attained stable electronic configurations.