Table of Contents
1. The Periodic table: Sequencing the Atoms
2. How many periods are in the periodic table?
3. Where are nonmetals located on the periodic table?
4. What is be in the periodic table?
5. How is the periodic table arranged?
6. How many elements are on the periodic table?
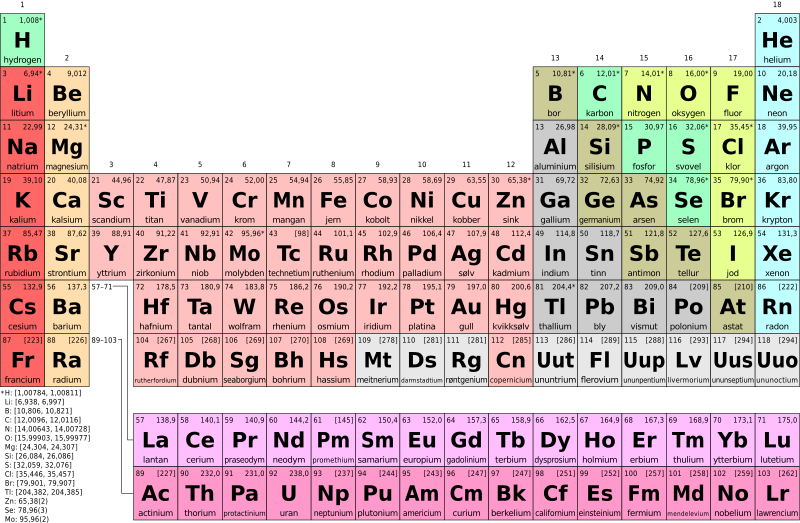
The Periodic table: Sequencing the Atoms
The periodic table is a tabular display of chemical elements. It is a graphic representation of the periodic law, which states that the properties and atomic structures of the chemical elements are a periodic function of their atomic number. This is why elements are placed in the periodic table according to their electronic configuration. It can be read like a book from left to right. The periodic table is based on the periodic law which states that the chemical elements exhibit periodic properties most especially their atomic numbers. It is a list of elements in order of increasing proton number. Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869 formulated the first widely accepted periodic table which is based on periodic law. The chemical properties are dependent on the atomic mass.
It consisted of rows and columns, the rows are called periods and the columns are called groups. Elements in the same column or group tend to have similar chemical properties. Each element in the same group contains the same number of valence electrons/electron (except Helium). For example, Group I-A (Alkali metals) elements have one electron in their last shell (Group number). Elements in the same period have the same number of shells. But as we move from left to right the shells are gradually filled with electrons.
Naturally existing elements are 94 while the rest of the elements in the periodic table were produced in the laboratory. There are some 118 elements in the periodic table. The 14 artificial elements are radioactive.
The elements are also classified into blocks, S, P,d,f, etc. This classification is based on the last electron(s) occupying the orbital shaped as s, p, d, or f, etc.
FAQs
How many periods are in the periodic table?
The periodic table is divided into seven periods. All discovered elements are divided into seven periods.
Where are nonmetals located on the periodic table?
Those elements which lack metallic properties such as electrical conductivity, ductility, and luster are considered nonmetals. These are some of the nonmetals which are in different periods and groups. They are Hydrogen, sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen, and member of halogen fluorine chlorine, bromine, and iodine. Astatine is very short-lived, highly radioactive and scarcity make it difficult to put in a category. Superheavy elements like oganesson and copernicium maybe not metallic because of data lacking regarding these elements. Noble gases such as helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon are nonmetals. Carbon, phosphorus, and selenium are also counted as nonmetals. Some are classified as metalloids boron; silicon and germanium; arsenic, antimony, and tellurium.
Now if we look at these elements they are in different periods and groups.
What is be in the periodic table?
“Be” is a symbol for the element Beryllium in the periodic table. For more info about Beryllium click the link below.
How is the periodic table arranged?
The periodic table is arranged on the basis of periodic law which is that the properties of the chemical elements exhibit a periodic dependence on their atomic numbers. The commonly accepted periodic table was proposed by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. It is base on the increasing atomic number.
How many elements are on the periodic table?
There are 118 known elements in the periodic table. 94 elements are those which can be found naturally. The remaining 24 elements are artificially created elements.